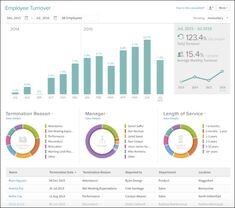
Employee Turnover Definitions & Calculations
Content

While it’s important to understand the total separations rate for your region or industry, you might be more concerned with your own business’s turnover rate. It is the percentage of employees who leave that particular workforce during a defined period of time, usually one year. In a way, the increasing turnover rates are a positive sign of a strong job market.

First, it can tell you whether your recruitment methods are working. If a significant number of your new employees leave because they found their job duties different to, or more complicated than, what they were expecting, perhaps you should consider reviewing your job descriptions. Investing more time and money developing your orientation process could help too, if employees leave because of cultural mismatches. You could also consider offering other employee engagement programs like parental leave or flexible working hours, if your employees struggle with work-life balance. Employees are important in any running of a business; without them the business would be unsuccessful. However, more and more employers today are finding that employees remain for approximately 23 to 24 months, according to the 2006 Bureau of Labor Statistics.
There Arent Enough Career Development Opportunities
We did not have access to employment records maintained by each system’s human resources departments; thus, we had no information on the type of employment separation category . Clinic leaders, however, reported low rates of involuntary termination and retirement in both systems. Inclusion of age and sex might have enhanced the explanatory power of our regression models, but is unlikely to have substantially changed the relationship between burnout or engagement and turnover. We grouped physicians and advanced practice clinicians for analysis.
Primary care costs are high and proportional to staff turnover and remoteness. Effectiveness of care decreases with higher turnover and use of short-term staff, such that higher staff turnover is always less cost-effective. If staff turnover in remote clinics were halved, the potential savings would be approximately A$32 million per annum. Staff turnover and retention were affected by management style and effectiveness, and employment of Indigenous staff. In conclusion, the high levels of primary care clinician and staff burnout and turnover observed in this and other studies are concerning. Our findings support the assertion that burnout and low employee engagement contribute to turnover among primary care clinicians, but not among staff.
It may reflect not only a negative “push” of burnout but a positive “pull” of career mobility and opportunities for professional growth. Millennials, who now make up the majority of the workforce, change jobs more frequently than previous generations. Compdata Surveys & Consulting tracked turnover rates from more than 30,000 US employers. Alarmingly, within the last seven years alone, voluntary turnover has risen steadily across all industries, increasing from 9.1% to a whopping 13.5% since 2010.
What Is The International Evidence Relating To Improving Remote Health Workforce Retention?
For the first time since the 2008 financial crisis, workers have plenty of opportunities for employment. This means that talented people should be able to find a position in an organization they like for a good salary.
How does Turnover impact the HR function?
When turnover is high, business leaders face increased costs associated with recruiting, selecting and training replacements. Other, more-difficult-to-quantify effects also arise, such as declines in productivity, morale, customer satisfaction and innovation.
A high turnover rate means that many of your employees – more than what’s expected in your line of business – have quit the organization over a certain period of time. What’s considered a high turnover rate depends on the industry you’re in. Different industries and countries have different expected turnover rates. But what if your business has a higher than average employee turnover rate? If your best people frequently leave your organization for greener pastures, you need to ask yourself why.
Business Owner’s Toolkit
A high employee turnover rate, the rate at which employees leave a business, can affect the bottom line of businesses of all sizes. However, the negative effect on small businesses can be particularly harsh due to limited resources and the investment in employees.
What are the effects of employee turnover?
If turnover rates are high, the immediate consequences are severe: loss of valuable knowledge and experience, loss of morale for those left, and loss of belief in the team’s competence and ability to perform. None of those are quick or easy to replace.
Because employees who are satisfied with their jobs generally don’t give them up, high turnover is usually indicative of a problem. Employee turnover calculations may also factor in different types of turnover, such as involuntary and voluntary, or even more specific reasons why employees leave, such as poor performance, absenteeism or employees accepting new jobs elsewhere. Turnover calculations are helpful to determine hiring costs, training requirements or estimating staff time devoted to recruitment activities. For example, your new hire turnover rate can offer a lot of insight.
That represents a 48% increase in voluntary turnover, clearly indicating the fact that employees are now in the driver’s seat in today’s highly competitive labor market. Gallup estimates Millennial turnover costs the US economy $30.5 billion a year.
In a larger sample, examination of each group separately might yield interesting information about the relationship of work experience and turnover. High rates of burnout and turnover in primary care are compelling problems. Our findings provide evidence that burnout contributes to turnover among primary care clinicians, but not among staff. Annual turnover rates of NT remote area nurses (148%) and Aboriginal health practitioners (80%) are very high and 12-month stability rates low (48% and 76%, respectively).
Navigating Uncertain Times
If an employer is said to have a high turnover rate relative to its competitors, it means that employees of that company have a shorter average tenure than those of other companies in the same industry. High turnover may be harmful to a company’s productivity if skilled workers are often leaving and the worker population contains a high percentage of novices.
- If an employer is said to have a high turnover rate relative to its competitors, it means that employees of that company have a shorter average tenure than those of other companies in the same industry.
- However, rates vary widely when compared over different periods of time and with different job sectors.
- High turnover may be harmful to a company’s productivity if skilled workers are often leaving and the worker population contains a high percentage of novices.
- Companies will often track turnover internally across departments, divisions, or other demographic groups, such as turnover of women versus men.
- Additionally, companies track voluntary turnover more accurately by presenting parting employees with surveys, thus identifying specific reasons as to why they may be choosing to resign.
Companies will often track turnover internally across departments, divisions, or other demographic groups, such as turnover of women versus men. Additionally, companies track voluntary turnover more accurately by presenting parting employees with surveys, thus identifying specific reasons as to why they may be choosing to resign. Many organizations have discovered that turnover is reduced significantly when issues affecting employees are addressed immediately and professionally. However, rates vary widely when compared over different periods of time and with different job sectors. For example, during the period, the annual turnover rate for all industry sectors averaged 39.6% prior to seasonal adjustments, while the Leisure and Hospitality sector experienced an average annual rate of 74.6% during this same period. External factors, such as financial needs and work-family balances due to environmental changes (e.g. economic crisis), can also lead to increased turnover rate. It was conducted in an urban region with a high cost of living, among employed clinicians and staff.
The findings may not be generalizable to other practice settings and regions. As in any survey, response bias may influence the validity of the results. Our 90% response rate is much higher than that reported in most surveys of health care workers, mitigating the potential that nonresponse bias may distort our findings. We relied on clinic leaders to update employment rosters annually at their clinic and had system leaders reconfirm roster data for 2016 to ensure accuracy.
Providing a stimulating workplace environment, which fosters happy, motivated and empowered individuals, lowers employee turnover and absentee rates. Promoting a work environment that fosters personal and professional growth promotes harmony and encouragement on all levels, so the effects are felt company wide. When accounting for the costs , the cost of employee turnover to for-profit organizations has been estimated to be between 30% to upwards of 150% of the employees’ remuneration package. Direct costs relate to the leaving costs, replacement costs and transitions costs, and indirect costs relate to the loss of production, reduced performance levels, unnecessary overtime and low morale. The true cost of turnover is going to depend on a number of variables including ease or difficulty in filling the position and the nature of the job itself. Estimating the costs of turnover within an organization can be a worthwhile exercise, especially since “turnover costs” are unlikely to appear in an organization’s balance sheets. Surveying employees at the time they leave an organization can also be an effective approach to understanding the drivers of turnover within a particular organization.