Feedback Inhibition In Metabolic Pathways

Content

ATP is required for the phosphorylation of glucose, creating a high-energy but unstable intermediate. This phosphorylation reaction causes a conformational change that allows enzymes to convert the phosphorylated glucose molecule to the phosphorylated sugar fructose.
The inner membrane contains an antiporter, the ADP/ATP translocase, which is an integral membrane protein used to exchange newly synthesized ATP in the matrix for ADP in the intermembrane space. This translocase is driven by the membrane potential, as it results in the movement of about 4 negative charges out across the mitochondrial membrane in exchange for 3 negative charges moved inside. However, it is also necessary to transport phosphate into the mitochondrion; the phosphate carrier moves a proton in with each phosphate, partially dissipating the proton gradient.
- Overproduction of lactic acid by anaerobic glycolysis can lead to lactic acidosis, a life-threatening medical condition.
- In some cells—notably in mature red blood cells—glycolysis is the only means of ATP production because of the lack of mitochondria.
- The latter pathway, anaerobic glycolysis, is believed to be the first process to have evolved in nature to produce adenosine triphosphate .
- is a linear metabolic pathway of enzyme-catalyzed reactions that converts glucose into two molecules of pyruvate in the presence of oxygen or two molecules of lactate in the absence of oxygen.
- Obligate ATP production via glycolysis also occurs in the absence of oxygen whether mitochondria are present or not.
- In most cells glycolysis converts glucose to pyruvate which is subsequently oxidized to carbon dioxide and water by mitochondrial enzymes.
The third step of glycolysis is the phosphorylation of fructose 6-phosphate, catalyzed by the enzyme phosphofructokinase. A second ATP molecule donates a phosphate to fructose 6-phosphate, producing fructose 1,6-bisphosphate and ADP as products. In this pathway, phosphofructokinase is a rate-limiting enzyme, and its activity is tightly regulated. It is allosterically activated by AMP when the concentration of AMP is high and when it is moderately allosterically inhibited by ATP at the same site. Citrate, a compound we’ll discuss soon, also acts as a negative allosteric regulator of this enzyme.
Carbohydrate Metabolism
Net gluconeogenesis occurs during starvation and after a meal high in fat and protein without carbohydrate. crista), which does not even allow the passage of small ions and so maintains a closed space within the cell. The electron-transferring molecules of the respiratory chain and the enzymes responsible for ATP synthesis are located in and on this inner membrane, while the space inside contains the enzymes of the TCA cycle (reactions to ).
The robust flux of glycolysis in cancer cells maintains high levels of intermediates required for the synthesis of macromolecules required for rapid growth and protection against reactive oxygen species. is a linear metabolic pathway of enzyme-catalyzed reactions that convert glucose into two molecules of pyruvate in the presence of oxygen or into two molecules of lactate in the absence of oxygen.
) occurs mainly in the liver and kidney cortex and to a lesser extent in the small intestine. The major substrates for gluconeogenesis include lactate, pyruvate, propionate, glycerol, and 18 of the 20 amino acids . Glucose cannot be synthesized from fatty acids, since they are converted by β-oxidation into acetyl coenzyme A , which subsequently enters the citric acid cycle and is oxidized to CO2.
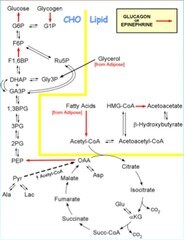
Gluconeogenesis is a continual process in carnivores and ruminant animals, therefore they have little need to store glycogen in their liver cells. Of the amino acids transported to liver from muscle during exercise and starvation, Ala predominates. b-Aminoisobutyrate, generated from pyrimidine degradation, is a gluconeogenic substrate. Glycolysis is the first of the main metabolic pathways of cellular respiration to produce energy in the form of ATP. Through two distinct phases, the six-carbon ring of glucose is cleaved into two three-carbon sugars of pyruvate through a series of enzymatic reactions. The first phase of glycolysis requires energy, while the second phase completes the conversion to pyruvate and produces ATP and NADH for the cell to use for energy.
Exercise Science
Feedback inhibition, where the end product of the pathway inhibits an upstream process, is an important regulatory mechanism in cells.The production of both amino acids and nucleotides is controlled through feedback inhibition. Additionally, ATP is an allosteric regulator of some of the enzymes involved in the catabolic breakdown of sugar, the process that creates ATP. In this way, when ATP is in abundant supply, the cell can prevent the production of ATP. On the other hand, ADP serves as a positive allosteric regulator for some of the same enzymes that are inhibited by ATP. Thus, when relative levels of ADP are high compared to ATP, the cell is triggered to produce more ATP through sugar catabolism. In the mitochondrion, pyruvate is oxidized by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex to the acetyl group, which is fully oxidized to carbon dioxide by the citric acid cycle .
is a linear metabolic pathway of enzyme-catalyzed reactions that converts glucose into two molecules of pyruvate in the presence of oxygen or two molecules of lactate in the absence of oxygen. The latter pathway, anaerobic glycolysis, is believed to be the first process to have evolved in nature to produce adenosine triphosphate . In some cells—notably in mature red blood cells—glycolysis is the only means of ATP production because of the lack of mitochondria. In most cells glycolysis converts glucose to pyruvate which is subsequently oxidized to carbon dioxide and water by mitochondrial enzymes. Obligate ATP production via glycolysis also occurs in the absence of oxygen whether mitochondria are present or not. Overproduction of lactic acid by anaerobic glycolysis can lead to lactic acidosis, a life-threatening medical condition. Finally, even when both mitochondria and oxygen are present, cancer cells preferentially produce ATP by the conversion of glucose to lactate by aerobic glycolysis.
After completing glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, the electron transport chain, and oxidative phosphorylation, approximately 30–38 ATP molecules are produced per glucose. During cellular metabolic reactions, or the synthesis and breakdown of nutrients, certain molecules must be altered slightly in their conformation to become substrates for the next step in the reaction series. In the very first steps of cellular respiration, glucose is broken down through the process of glycolysis.
Glucose Oxidation Energy Balance
Overall, the process of glycolysis produces a net gain of two pyruvate molecules, two ATP molecules, and two NADH molecules for the cell to use for energy. Following the conversion of glucose to pyruvate, the glycolytic pathway is linked to the Krebs Cycle, where further ATP will be produced for the cell’s energy needs.

NADH and FADH2 are recycled (to NAD+ and FAD, respectively), generating additional ATP by oxidative phosphorylation. The oxidation of NADH results in the synthesis of 2–3 equivalents of ATP, and the oxidation of one FADH2 yields between 1–2 equivalents of ATP. Although the citric acid cycle itself does not involve molecular oxygen, it is an obligately aerobic process because O2 is used to recycle the NADH and FADH2 and provides the chemical energy driving the process. The citric acid cycle is controlled through the enzymes that catalyze the reactions that make the first two molecules of NADH. These enzymes are isocitrate dehydrogenase and α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase.
In addition, the last three carbon atoms of the odd-chain fatty acids generate proprionyl CoA during β-oxidation and are thus partly gluconeogenic. The remainder of the pathway is simply a reversal of the enzymes of glycolysis, which is responsible for the breakdown of glucose. Gluconeogenic enzymes are present in the cytosol, mitochondria, and endoplasmic reticulum of the tissues in which this pathway is present.
The oxidative phosphorylation systems of bacteria are similar in principle but show a greater diversity in the composition of their respiratory carriers. Figure 11 Metabolic pathways are a series of reactions catalyzed by multiple enzymes.
Even when oxygen is available, cancer cells produce much of their ATP by glycolysis. The ability to produce sufficient ATP by a pathway that does not require oxygen gives cancer cells a selective advantage over normal cells. refers to synthesis of new glucose from noncarbohydrate precursors, provides glucose when dietary intake is insufficient or absent. It also is essential in the regulation of acid-base balance, amino acid metabolism, and synthesis of carbohydrate derived structural components. The precursors of gluconeogenesis are lactate, glycerol, amino acids, and with propionate making a minor contribution.
Fructose is a necessary intermediate for glycolysis to move forward. In this example, the exergonic reaction of ATP hydrolysis is coupled with the endergonic reaction of converting glucose for use in the metabolic pathway. Gluconeogenesis supplies the needs for plasma glucose between meals.
Gluconeogenic substrates include glycerol, lactate, propionate, and certain amino acids. PEP carboxykinase catalyzes the rate-limiting reaction in gluconeogenesis. The dicarboxylic acid shuttle moves hydrocarbons from pyruvate to PEP in gluconeogenesis.
The gluconeogenesis pathway consumes ATP, which is derived primarily from the oxidation of fatty acids. The pathway uses several enzymes of the glycolysis with the exception of enzymes of the irreversible steps namely pyruvate kinase, 6-phosphofructokinase, and hexokinase. The irreversible reactions of glycolysis are bypassed by four alternate unique reactions of gluconeogenisis. Most of the ATP synthesized in the mitochondria will be used for cellular processes in the cytosol; thus it must be exported from its site of synthesis in the mitochondrial matrix. ATP outward movement is favored by the membrane’s electrochemical potential because the cytosol has a relatively positive charge compared to the relatively negative matrix.
Atp
However, in some cells, most notably mature red blood cells, glycolysis is the only means of ATP production because of the lack of mitochondria. In the absence of oxygen, glycolysis is the only option that cells have for the production of ATP from glucose. Overproduction of lactic acid by anaerobic glycolysis leads to lactic acidosis, a life-threatening condition. Many cancer cells have an exceptionally high enzymatic capacity for glycolysis.



