Levels Of Workforce Planning

Content

This lets the business manage costs while adapting to meet growing customer demands. In a nutshell, though, workforce planning is the process of ensuring the organization has the right number of people with the right skills, in the right place, at the right time to deliver on business goals.
The organization’s strategy, including its mission or “why,” core values and culture as well as its competitive strategy, has implications for not only human resource structure, policies and practices but how roles are designed and valued. If you were to list the most important words describing a successful organization, the word planning would definitely be in the mix. To be more specific, strategic workforce planning is a key characteristic of well-operating organizations. All of the most successful businesses use strategic workforce planning to forecast the future of the market, analyze performance metrics, and prevent damage to their corporate image. Strategic human resource management is “critical importance of human resources to strategy, organizational capability to adapt to change and the goals of the organization”[citation? In other words, this is a strategy that intends to adapt the goals of an organization and is built off of other theories such as the contingency theory as well as institutional theory which fit under the umbrella of organizational theory. These theories look at the universalize, contingency and configuration perspectives to see the effect of human resource practices in organizations.
Latest Techtarget Resources
You might ask your executive team to provide you with an annual and business plan. This should feature the projected needs for how to carry out goals, including the number of employees required.
In today’s talent-based economy, the workforce itself is arguably the most important tangible asset of most organizations. Despite its importance, this asset is often not carefully planned, measured or optimized. This means that many organizations are not sufficiently aware of the current or future workforce gaps that will limit execution of business strategy. Yet at the same time, boards of directors, CEOs and chief human resources officers will frequently declare that workforce planning and data- driven decision-making is a top priority for their organizations. Organizations need an approach that moves workforce planning from the domain of “futurists,” where only a few people live, to the domain of operational effectiveness, where management is accustomed to spending its time and energy. Though strategic workforce planning is in no doubt essential, it is far from a simple process. There is now an approach for high-performance organizations to develop and sustain high-quality workforce planning programs, and break down the traditional barriers to effective workforce planning.
Benefits Of Strategic Workforce Planning
Two recent trends serve to moderate—and sometimes even eliminate—these potential roadblocks. The first is a broad-scale acceptance of data-driven decision-making that is infusing the culture of organizations and making workforce planning inherently more attractive.

Strategic workforce planning is created by designing a process within your organization that proactively anticipates current and future hiring needs. This will ensure your organization has the resources needed to meet its business goals. At this point, gather all the relevant information for your workforce planning process. Request your agency’s strategic plan for the time that you plan to explore.
Why Is Workforce Planning Important?
Knowing exactly where they need to hire can better focus human resources teams — freeing up time to hire the most sought-after talent within specific industries and allowing organisations to stay one step ahead of their competition. Jennifer leads the customer value team at Visier that helps organizations implement, use, adopt and get value from analytics and workforce planning solutions. Her team has successfully guided Fortune 1000 companies to connect their workforce strategy to the use of analytics to make an impact on the business. Prior to Visier, Jennifer led a workforce reporting and analytics team at an insurance organization in Vancouver, and she has held organizational change management and project management roles at SAP and Shell. Outside of work, she’s kept busy by two energetic sons and enjoys travelling and the outdoors.
What are the 5 key elements of workforce planning?
INTRODUCTION. Workforce planning is the systematic process for identifying and.
OPM’S 5-STEP. WORKFORCE.
Step 1: Set. Strategic.
Step 2: Analyze. Workforce,
Step 3: Develop. Action Plan.
Implement. Action Plan.
Step 5: Monitor, Evaluate, and Revise.
By taking this approach, a high performance organization will be able to conduct gap analysis on the work unit, business unit, and on the organization as a whole. At the work unit level, managers will be better at planning and responding to changes in the business. Managers will also be able to make data-driven decisions that move gradually from blanket HR policies to targeted HR interventions based on the importance of a role or the performance of the individual. Business units and the total organization will also reap the benefits of the workforce planning pro- gram. Finance and real estate will have the information needed to construct their budgets. Human Resources will be able to make better high-level decisions about recruitment, development, redeployment, and transition pro- grams. And, senior leadership will be able to monitor the people health of the organization and the organizational capacity to meet present and future business objectives.
What Are The Benefits Of Strategic Workforce Planning?
The objective of human resource planning is to ensure the best fit between employees and jobs, while avoiding workforce shortages or spares. The three key elements of the HR planning process are forecasting labour demand, analysing present labour supply, and balancing projected labour demand and supply. Human resource planning is a process that identifies current and future human resources needs for an organization to achieve its goals. Human resource planning should serve as a link between human resource management and the overall strategic plan of an organization. Ageing workers population in most western countries and growing demands for qualified workers in developing economies have underscored the importance of effective human resource planning. We’ve previously discussed the strategic planning process and the role that HR management plays in supporting the planning and implementation process. As stated in Human Resources Today, the role of human resource management is to ensure that an organization has the talent—the right combination of skills, knowledge, aptitude and attitude—to achieve its strategic goals.
What is workforce planning and employment?
Workforce planning is the process an organization uses to analyze its workforce and determine the steps it must take to prepare for future staffing needs. These factors may determine whether future skill needs will be met by recruiting, by training or by outsourcing the work.
The organization must foster a data-driven planning culture and be willing to value the planning process as much as the actual plan. The organization must also invest in workforce planning technology that supports predictive supply analytics, bottom-up demand planning, employee- level action-planning, and summarization of gaps. It also can pinpoint staffing gaps, which job functions and processes are no longer necessary and whether workers should be reassigned to other roles. Workforce planning also includes developing and putting into practice policies to help employees remain satisfied with their jobs.
The second involves recent advances in predictive analytics and modeling technology. These advances provide more compelling near-term actionable information about granular employee-level supply risk, while simultaneously helping with demand-based scenario planning. Coupled together, these trends have a profound ability to move workforce planning from a “nice-to-have” status to a critical program for high-performance organizations. Diagram 1 outlines a workforce planning process that combines end-user-based demand planning with predictive supply analytics. Addressing current workforce gaps – Analyzing the skills of your current employees can provide insights into the skill or resource gaps that you currently have within your business. Through this evaluation, you will be able to identify the gaps between your current workers’ competencies and what you’ll need in the future to reach your goals. Using that information you can ensure you acquire top talent with the skills required for your company’s success.
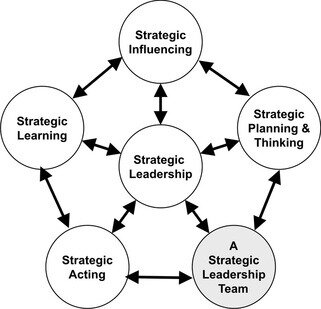
Strategic workforce planning is a process within a business or organisation that anticipates the current human capital needs not only for today but for the future. By implementing a strategic workforce plan, a business can ensure that it has the resources in place to achieve its long-term goals. These strategies and programs are monitored and evaluated on a regular basis to ensure that they are moving the organizations in the desired direction, including closing employee competency gaps, and corrections are made as needed. This Strategic HR Planning and evaluation cycle is depicted in the diagram to the right. Human resource planning is the ongoing process of systematic planning to achieve the best use of an organisation’s most valuable asset – its human resources.
- Organizations need an approach that moves workforce planning from the domain of “futurists,” where only a few people live, to the domain of operational effectiveness, where management is accustomed to spending its time and energy.
- In today’s talent-based economy, the workforce itself is arguably the most important tangible asset of most organizations.
- Though strategic workforce planning is in no doubt essential, it is far from a simple process.
- This means that many organizations are not sufficiently aware of the current or future workforce gaps that will limit execution of business strategy.
- Yet at the same time, boards of directors, CEOs and chief human resources officers will frequently declare that workforce planning and data- driven decision-making is a top priority for their organizations.
- Despite its importance, this asset is often not carefully planned, measured or optimized.
Ultimately, strategic workforce planning is a continuous, dynamic process that helps leaders ensure talent decisions are aligned with where the business needs to go in the future. The second trend that is being recognised is the need for workforce planning to include skills data and to support career pathing and internal mobility. Talent mobility focuses on companies understanding how to optimise their organisation for productivity, growth and success – all while keeping their employees engaged in both their current and future career.
Strategic workforce planning involves ensuring that an organization has the right people who have the right skills at the right time, according to CQ University Australia. The workplace planning model helps your HR team examine the gaps in your present workforce. Medium-term workforce planning is often referred to as operational. It usually covers the next 12 months and aligns with the annual business planning cycle to deliver business objectives. Longer term planning covers an 18-month to 3-year forecast period and looks at the workforce implications attached to an organization’s vision for the future.
Discuss factors with project leaders regarding the duration of engagement with new employees. Using workforce planning software, organizations can schedule employee hours and shifts using accurate labor and sales forecasting that matches demand to labor needs. Workforce planning technology can also help managers better prepare for retirements and design a talent acquisition strategy to replace retiring employees. Once a strategic workforce plan is in place, businesses can identify gaps within their current talent pool.
This can also be viewed as how human resource practices fit vertically or horizontally in an organization. This theory also involves looking at the value of human capital as well as social capital both in and outside of organizations and how this affects human resource practices. Human capital being knowledge and skills of individuals working for the organization and social capital is based on the character and value of relationships in and out of the organization. “Colbert suggests that SHRM should focus on the interactions and processes of the organization’s social system—the intentions, choices and actions of people in the system and on HR systems as a coherent whole.” Another one of our customers (a 50,000-employee financial services company) uses a monthly planning process to capture workforce demand for the different groups within the organization. After analyzing the Total Cost of Workforce , planners compare scenarios for future states of the workforce and see how the cost of contractors or full-time employees would compare over time.