Social Security And Medicare

Content

For 2018 I am a W2 employee and my wife is now a 1099 contract employee. I am trying to figure our estimated tax payments for 2018. On line 13 of 1040-ES it asks for “Income tax withheld and estimated to be withheld during 2018”. Since I am a W2 employee my employer withholds federal income tax, medicare tax, and social security tax. I am unsure whether to include all three of these withholdings or just the federal income tax portion. If you are self-employed, you are responsible for withholding your own taxes and sending them to the IRS.

Withholding of tax on wages includes income tax, social security and medicare, and a few taxes in some states. Certain minimum amounts of wage income are not subject to income tax withholding. Wage withholding is based on wages actually paid and employee declarations on federal and state Forms W-4. Social Security tax withholding terminates when payments from one employer exceed the maximum wage base during the year.
Information Menu
Amounts of tax withheld are determined by the employer. Tax rates and withholding tables apply separately at the federal, most state, and some local levels. The amount to be withheld is based on both the amount wages paid on any paycheck and the period covered by the paycheck. Federal and some state withholding amounts are at graduated rates, so higher wages have higher withholding percentages. Withheld income taxes are treated by employees as a payment on account of tax due for the year, which is determined on the annual income tax return filed after the end of the year .
- The amount to be withheld is based on both the amount wages paid on any paycheck and the period covered by the paycheck.
- Withholding for allowances are calculated based on the assumption of a full year of wages.
- Federal and some state withholding amounts are at graduated rates, so higher wages have higher withholding percentages.
- Amounts of tax withheld are determined by the employer.
- Tax rates and withholding tables apply separately at the federal, most state, and some local levels.
- Income tax withheld on wages is based on the amount of wages less an amount for declared withholding allowances .
However, if you had too much withheld, you may be entitled to a credit on your tax return. Taxpayers are required to pay at least 90 percent of their total tax liability in installments prior to April 15.
Income tax withheld on wages is based on the amount of wages less an amount for declared withholding allowances . Withholding for allowances are calculated based on the assumption of a full year of wages.
How To Calculate Fica Withholding
Nonstudent employees are generally subject to FICA tax withholding. Social Security is withheld on taxable gross income up to a certain wage limit each year, but there is no wage limit for Medicare withholding. The current rates of withholding are 6.2% for OASDI and 1.45% for Medicare. However, some federal employees and police department employees only have Medicare taxes withheld. When an employee’s wages exceed $200,000, an additional .9% Medicare tax is withheld beginning with the pay period when the wages go over $200,000 through the end of the calendar year. Employers are required to withhold 7.65 percent of the first $94,200 of an employee’s income for FICA taxes. Employers are also required to match that amount for every employee, so that the total FICA contribution is 15.3 percent.
Self-employed persons are required to pay both the employer and employee portions of the FICA tax. The amount of regular income tax that must be withheld from an employee’s paycheck depends on the individual’s tax status. Ideally, the total income tax withheld should come close to equaling the employee’s overall tax liability at the end of the year. To the extent the employer does not withhold the 0.9 percent Medicare surtax, the employee must pay the tax.
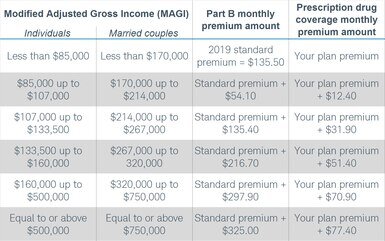
Withholdings in excess of tax so determined are refunded. The amount of tax withheld is based on the amount of payment subject to tax.
Who Can Get A Refund For Fica Overpayment
Federal income is calculated using the remaining 92.35 percent as your starting point instead of gross wages. The amount that is withheld from an employee’s paycheck in order to pay income taxes is determined based on the person’s income level and the number of exemptions that the person claims. Withholding is usually done in standard amounts based on formulas provided by the IRS. Employees can adjust their income tax withholding by filing Form W-4 with their employer and designating the number of withholding allowances they wish to claim. It is not advisable to overpay taxes–even though the extra amount is eventually refunded to the taxpayer–because it is like giving the government an interest-free loan. At the same time, it is not advisable to underpay taxes because it may be difficult to come up with a lump-sum payment when it is due on April 15. In addition, a taxpayer who underpays his or her income taxes by more than 10 percent may face a penalty and have to pay the government interest on the funds owed.
Tax withholding refers to the portion of an employee’s gross wages that is retained by an employer for remittance to the Internal Revenue Service . Many states and some cities and municipalities also apply taxes and in some cases these taxes too must be withheld by employers. When you earn money from working, your employer withholds a portion of your paycheck for various taxes, including federal income taxes, state incomes taxes and payroll taxes. The Social Security payroll tax rate equals 7.65 percent as of 2018. You can’t claim any income tax benefit for the Social Security taxes withheld, though the Social Security taxes withheld determine your Social Security benefits in retirement.
Do You Take Withholding Tax Off Of A Paycheck Before Or After Fica?
If they do not, they may be subject to a penalty. However, the penalty is waived for taxpayers who pay at least as much in total taxes as they had owed the previous year, or for whom the amount underpaid is less than $500. Since the IRS calculates the amount owed quarterly, a large lump-sum payment in the fourth quarter will not enable a taxpayer to escape penalties. For this reason, taxpayers who see a significant underpayment problem looming should have additional taxes withheld by their employers.
Self-employment taxes are handled a bit differently than withholding for employee wages. Start with total earnings calculated by subtracting business expenses from revenues. Self-employed people pay both the employee’s FICA tax and the matching employer portion. As of 2014 this meant withholding 15.3 percent of earnings. The employer portion isn’t subject to federal income tax. Subtract half of the self-employment FICA tax, or 7.65 percent, for the total earnings to find net earnings.
Employees who anticipate being under-withheld for the Medicare surtax can make estimated payments or they can request additional income tax withholding on Form W-4. The employee can then apply the additional income tax withheld against Medicare surtax liability on his or her Form 1040, U.S. Companies and individuals who make certain types of payments to foreign persons must withhold federal income tax on those payments.
Are unemployment benefits subject to federal income tax?
Federal income tax is withheld from unemployment benefits at a flat rate of 10%. 3 Depending on the number of dependents you have, this might be more or less than what an employer would have withheld from your pay. You can use Form W-4V, Voluntary Withholding Request, to have taxes withheld from your benefits.
Foreign persons include nonresident aliens, foreign corporations, and foreign partnerships. Payments subject to withholding include compensation for services, interest, dividends, rents, royalties, annuities, and certain other payments. Tax is withheld at 30% of the gross amount of the payment.
An employee may request that his or her employer withhold and send to the IRS as large a percentage of his or her gross income as desired. To avoid a penalty, the total tax withheld must reach 90 percent of what will be owed in the current year or 100 percent of what was owed in the previous year.