What Is a Contra Account? The Motley Fool
Content

Contra Asset Account – A contra asset account is an asset that carries a credit balance and is used to decrease the balance of another asset on the balance. Whereas assets normally have positive debit balances, contra assets, though still reported along with other assets, have an opposite type of natural balance. As you saw in the example, contra accounts can be an important part of your financial statement analysis, but they are hard to find. Companies bury them in the footnotes and often don’t break out the actual calculation.
The difference between an asset’s account balance and the contra account balance is known as the book value. Home Depot reports that returns are estimated at the time of the sale based on historic returns numbers. The amount is not reported, and the net sales amount is reported on the income statement. The allowance method of accounting allows a company to estimate what amount is reasonable to book into the contra account. The percentage of sales method assumes that the company cannot collect payment for a fixed percentage of goods or services that it has sold. The allowance for doubtful accounts is not specifically reported, but the 10(K) reported that the allowance is immaterial to the amount.
Contra Asset, Contra Liability and Contra Equity
Contra revenue accounts reduce revenue accounts and have a debit balance. Contra asset accounts include allowance for doubtful accounts and accumulated depreciation. Contra asset accounts are recorded with a credit balance that decreases the balance of an asset. A key example of contra liabilities include discount on notes or bonds payable.
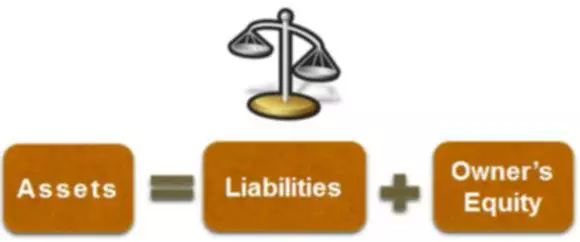
There are four key types of contra accounts—contra asset, contra liability, contra equity, and contra revenue. Contra assets decrease the balance of a fixed or capital asset, carrying a credit balance. Contra liabilities reduce liability accounts and carry a debit balance. Contra equity accounts carry a debit balance reduce equity accounts.
Everything You Need To Master Financial Modeling
Still, the dollar amounts are separately broken out in the supplementary sections most of the time for greater transparency in financial reporting. Contra accounts are confusing at first, but, with a little study, understanding them becomes second nature. Let’s go over how they work and what the main types are, and then finish with an example. We can see how the $10,000 allowance for doubtful accounts offsets the $100,000 A/R account from our illustrative example above (i.e. the account decreases the carrying value of A/R). Volatility profiles based on trailing-three-year calculations of the standard deviation of service investment returns.
This depreciation is saved in a contra asset account called accumulated depreciation. The accumulated depreciation account has a credit balance and is used to reduce the carrying value of the equipment. The balance sheet would report equipment at its historical cost and then subtract the accumulated depreciation. Key examples of contra asset accounts include allowance for doubtful accounts and accumulated depreciation.
Types of Contra Accounts
Last, for contra revenue accounts there are sales discounts, sales allowances, or sales returns. These contra revenue accounts tend to have a debit balance and are used to calculate net sales. A contra liability is an account in which activity is recorded as a debit balance is used to decrease the balance of a liability. Contra Liability a/c is not used as frequently as contra asset accounts. It is not classified as a liability since it does not represent a future obligation.

If accounts receivable is $40,000 and allowance for doubtful accounts is $4,000, the net book value reported on the balance sheet will be $36,000. The equity section of the balance sheet is where the shareholder’s claims to assets are reported. The main contra equity account is treasury stock, which is the balance of all stock repurchased by the company. When a company repurchases shares, it increases the fractional ownership of all remaining shareholders.
What Cash Receipts Are Not Revenue?
When the account receivable is written off, it is added to bad debt expense on the income statement and placed in the contra account. If a company has a high or fast-growing allowance as a percentage of accounts receivable, keep a close eye on it. It could be growing with bad accounts, and cash flow will be affected. The treasury stock account will have a debit balance of $100,000, representing the cost of the repurchased shares. This amount will reduce the company’s total equity on the balance sheet.
If a contra account is not used, it can be difficult to determine historical costs, which can make tax preparation more difficult and time-consuming. The contra equity account treasury stock is reported right on the balance sheet. Home Depot has repurchased more than $72 billion of stock to date, with around $7 billion coming during this accounting period.
- Examples of contra equity accounts include the treasury stock account, the owners’ drawing account, and a dividend account.
- Still, it is important when possible to consider how the net accounts are calculated and be wary of companies that are reporting a ton of bad debts.
- Contra accounts provide more detail to accounting figures and improve transparency in financial reporting.
- Contra accounts are used to reduce the original account directly, keeping financial accounting records clean.
- Contra accounts exist when the account reported on the balance sheet needs to be reduced by a different account to show its true value.
Instead, it is reported at its full amount with an allowance for bad debts listed below it. Maybe more importantly, it shows investors and creditors what percentage of receivables the company is writing off. When a contra asset account is first recorded in a journal entry, the offset is to an expense. For example, an increase in the form of a credit to allowance for doubtful accounts is also recorded as a debit to increase bad debt expense. Accountants use contra accounts rather than reduce the value of the original account directly to keep financial accounting records clean.
To drum up interest in the bond, the company will sell it at a discount. For example, a bond with a principal amount of $1,000 may be sold for only $950. The bond is listed on the balance sheet at the full amount of $1,000, but the cash received is just $950, so a contra liability for the discount is listed to make the entry balance.
Examples include the owner’s drawing account, a dividend account, and the treasury stock account. A contra equity account has a debit balance (as opposed to equity that has a credit balance). Contra accounts are used to reduce the value of the original account directly to keep financial accounting records clean.
Business owners should understand the functions of contra accounts and their importance to maintaining accurate financial records. Contra accounts exist when the account reported on the balance sheet needs to be reduced by a different account to show its true value. The balance sheet will show a gross fixed assets value, a contra account value for accumulated depreciation, and a net value. All three values can be useful for investors depending on what they’re looking for. A contra account that is used to adjust an owners’ equity (stockholders’ equity) account by reducing it to arrive at its net value. Examples of contra equity accounts include the treasury stock account, the owners’ drawing account, and a dividend account.
The purpose of a contra equity account is to reduce the total equity shown on the balance sheet by reflecting specific adjustments or deductions related to the equity of the company. Transactions made to contra accounts are presented on a company’s financial statements under the related account. Contra accounts are important because they allow a company to follow the matching principle by recording an expense initially in the contra asset account. The contra asset account is later reduced when the expense is recorded.
Allowance for doubtful accounts reduce accounts receivable, while accumulated deprecation is used to reduce the value of a fixed asset. In order to balance the journal entry, a debit will be made to the bad debt expense for $4,000. Although the accounts receivable is not due in September, the company still has to report credit losses of $4,000 as bad debts expense in its income statement for the month.
This make sense because Home Depot wouldn’t be carrying accounts receivable with long payment terms. Most accounts receivable would just be the time between purchase and credit card settlement. Accounts receivable (A/R) has a debit balance, but the allowance for doubtful accounts carries a credit
balance. Those who are struggling with recording contra accounts may benefit from utilizing some of the best accounting software currently available. For example, if a piece of heavy machinery is purchased for $10,000, that $10,000 figure is maintained on the general ledger even as the asset’s depreciation is recorded separately.
Contra Liability Account – A contra liability account is a liability that carries a debit balance and decreases other liabilities on the balance sheet. Let’s consider a fictional example of a company called “TechGuru Inc.” to illustrate the use of a contra equity account in financial accounting. For example, accumulated depreciation is a contra asset that reduces the value of a company’s fixed assets, resulting in net assets. However, that $1.4 billion is used to reduce the balance of gross accounts receivable. Therefore, contra accounts, though they represent a positive amount, are used to net reduce a gross amount. For this reason, contra accounts are primarily seen as having negative balances because they are used to reduce the balance of another account.